1.MCP架构概览:深入理解模型上下文协议 #
本文深入探讨MCP的核心
2.🎯 协议范围 #
MCP(Model Context Protocol)包含以下📚 核心组件:
| 组件 | 描述 | 链接 |
|---|---|---|
| MCP规范 | 协议实现的详细规范文档 | 查看规范 |
| MCP SDKs | 多语言开发工具包 | 查看SDK |
| 开发工具 | 调试和测试工具 | MCP检查器 |
| 参考实现 | 官方服务器示例 | 参考服务器 |
⚠️ 重要说明:MCP专注于上下文交换协议,不规定AI应用如何使用LLM或管理上下文。
3.🏗️ 核心概念 #
3.1 参与者角色 #
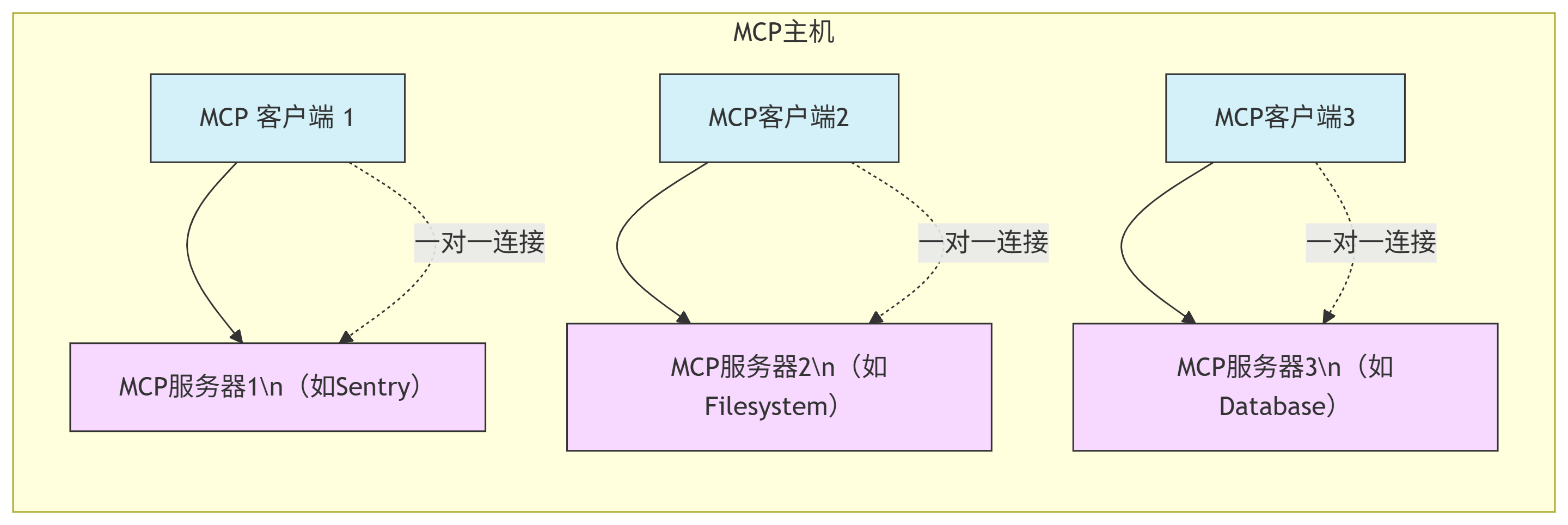
MCP采用客户端-服务器架构,包含三个核心角色:
3.1.1. MCP主机(AI应用) #
- 职责:协调和管理多个MCP客户端
- 示例:Claude桌面版、VS Code、LlamaIndex
- 特点:为每个MCP服务器创建独立的客户端连接
3.1.2. MCP客户端 #
- 职责:维持与MCP服务器的连接
- 功能:从服务器获取上下文数据
- 特点:每个客户端与服务器保持一对一连接
3.1.3. MCP服务器 #
- 职责:为客户端提供上下文数据
- 类型:本地服务器(STDIO)和远程服务器(HTTP)
- 示例:文件系统服务器、数据库服务器、API服务器
3.2 架构示意图 #
3.3 连接类型 #
| 类型 | 传输方式 | 特点 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 本地服务器 | STDIO | 高性能、无网络开销 | 文件系统、本地工具 |
| 远程服务器 | HTTP | 支持远程访问、标准认证 | 云服务、API集成 |
4.🏛️ 架构层次 #
MCP采用分层架构设计,包含两个核心层次:
4.1 数据层(内层) #
定义:基于JSON-RPC 2.0的客户端-服务器通信协议
核心功能:
- 🔄 生命周期管理:连接初始化、能力协商、连接终止
- 🛠️ 服务器功能:工具、资源、提示词提供
- 🎯 客户端功能:采样、启发、日志记录
- 📢 实用功能:实时通知、进度追踪
4.2 传输层(外层) #
定义:管理客户端与服务器间的通信通道和身份验证
支持机制:
- 标准输入输出传输:本地进程间通信
- 🌐 可流式HTTP传输:远程服务器通信
5.📊 数据层协议详解 #
5.1 协议基础 #
MCP采用JSON-RPC 2.0作为底层通信协议:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "initialize",
"params": {
"protocolVersion": "2025-06-18",
"capabilities": {
"tools": {}
},
"clientInfo": {
"name": "example-client",
"version": "1.0.0"
}
}
}5.2 核心原语 #
MCP定义了三种核心原语,服务器可以暴露:
5.2.1 工具(Tools) #
功能:AI应用可调用的可执行函数
# 工具定义示例
{
"name": "com.example.weather/current",
"title": "获取当前天气",
"description": "获取指定城市的当前天气信息",
"inputSchema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {"type": "string", "description": "城市名称"},
"units": {"type": "string", "enum": ["metric", "imperial"]}
},
"required": ["location"]
}
}5.2.2 资源(Resources) #
功能:为AI应用提供上下文信息的数据源
# 资源定义示例
{
"name": "com.example.filesystem/document",
"title": "文档内容",
"description": "文件系统中的文档内容",
"mimeType": "text/plain"
}5.2.3 提示词(Prompts) #
功能:可复用的交互模板
# 提示词定义示例
{
"name": "com.example.assistant/system",
"title": "系统提示",
"description": "AI助手的系统级提示词",
"prompt": "你是一个专业的编程助手..."
}5.3 客户端原语 #
MCP还定义了客户端可以暴露的基础原语:
5.3.1 采样(Sampling) #
功能:允许服务器请求语言模型补全
# 采样请求示例
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 4,
"method": "sampling/complete",
"params": {
"prompt": "请解释什么是MCP协议",
"maxTokens": 100
}
}5.3.2. 启发(Elicitation) #
功能:允许服务器向用户请求更多信息
# 启发请求示例
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 5,
"method": "elicitation/request",
"params": {
"message": "请确认是否要删除这个文件?",
"type": "confirmation"
}
}5.3.3. 日志记录(Logging) #
功能:服务器向客户端发送日志消息
# 日志记录示例
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "logging/log",
"params": {
"level": "info",
"message": "工具执行成功"
}
}6.🔄 完整示例:MCP交互流程 #
6.1 步骤1:初始化(生命周期管理) #
客户端发送初始化请求:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "initialize",
"params": {
"protocolVersion": "2025-06-18",
"capabilities": {
"tools": {}
},
"clientInfo": {
"name": "example-client",
"version": "1.0.0"
}
}
}服务器响应:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"result": {
"protocolVersion": "2025-06-18",
"capabilities": {
"tools": {"listChanged": true},
"resources": {}
},
"serverInfo": {
"name": "weather-server",
"version": "1.0.0"
}
}
}客户端发送就绪通知:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "notifications/initialized"
}6.2 步骤2:工具发现 #
客户端请求工具列表:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 2,
"method": "tools/list"
}服务器响应工具列表:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 2,
"result": {
"tools": [
{
"name": "com.example.weather/current",
"title": "获取当前天气",
"description": "获取指定城市的当前天气信息",
"inputSchema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市名称"
},
"units": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["metric", "imperial"],
"default": "metric"
}
},
"required": ["location"]
}
}
]
}
}6.3 步骤3:工具执行 #
客户端调用工具:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 3,
"method": "tools/call",
"params": {
"name": "com.example.weather/current",
"arguments": {
"location": "San Francisco",
"units": "imperial"
}
}
}服务器返回执行结果:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 3,
"result": {
"content": [
{
"type": "text",
"text": "旧金山当前天气:晴天,温度72°F,湿度65%"
}
]
}
}6.4 步骤4:实时通知 #
服务器发送工具列表变更通知:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "tools/list_changed",
"params": {
"tools": [
{
"name": "com.example.weather/forecast",
"title": "天气预报",
"description": "获取未来几天的天气预报"
}
]
}
}7.💻 完整代码示例 #
7.1 MCP服务器实现 #
7.1.1 weather_server.py #
# 导入json模块,用于处理JSON数据
import json
# 导入sys模块,用于标准输入输出
import sys
# 从typing模块导入类型注解
from typing import Any, Dict, List
# 定义天气服务器类
class WeatherServer:
"""天气服务器类"""
# 构造函数,初始化工具字典
def __init__(self):
# 定义支持的工具及其元数据和输入模式
self.tools = {
"com.example.weather/current": {
"name": "com.example.weather/current",
"title": "获取当前天气",
"description": "获取指定城市的当前天气信息",
"inputSchema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {"type": "string", "description": "城市名称"},
"units": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["metric", "imperial"],
"default": "metric",
},
},
"required": ["location"],
},
},
"com.example.weather/forecast": {
"name": "com.example.weather/forecast",
"title": "天气预报",
"description": "获取未来几天的天气预报",
"inputSchema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {"type": "string", "description": "城市名称"},
"days": {
"type": "integer",
"minimum": 1,
"maximum": 7,
"default": 3,
},
},
"required": ["location"],
},
},
}
# 处理JSON-RPC请求的方法
def handle_request(self, request: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""处理JSON-RPC请求"""
# 获取请求的方法名
method = request.get("method")
# 获取请求的id
request_id = request.get("id")
# 获取请求参数,默认为空字典
params = request.get("params", {})
# 如果方法为initialize,返回初始化响应
if method == "initialize":
# 初始化响应
return {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": request_id,
"result": {
"protocolVersion": "2025-06-18",
"capabilities": {
"tools": {"listChanged": True},
"resources": {},
},
"serverInfo": {"name": "weather-server", "version": "1.0.0"},
},
}
# 如果方法为tools/list,返回工具列表
elif method == "tools/list":
# 工具列表响应
return {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": request_id,
"result": {"tools": list(self.tools.values())},
}
# 如果方法为tools/call,调用指定工具
elif method == "tools/call":
# 获取工具名称
name = params.get("name")
# 获取工具参数
arguments = params.get("arguments", {})
try:
# 调用工具方法
result = self.call_tool(name, arguments)
# 返回调用结果
return {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": request_id,
"result": {"content": result},
}
# 捕获异常,返回错误信息
except Exception as e:
return {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": request_id,
"error": {"code": -32603, "message": str(e)},
}
# 其他未知方法,返回方法未找到错误
else:
return {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": request_id,
"error": {"code": -32601, "message": f"Method {method} not found"},
}
# 工具调用方法,根据工具名称和参数执行相应操作
def call_tool(self, name: str, arguments: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""执行工具调用"""
# 如果调用的是获取当前天气工具
if name == "com.example.weather/current":
# 获取城市名称,默认为“未知城市”
location = arguments.get("location", "未知城市")
# 获取温度单位,默认为“metric”
units = arguments.get("units", "metric")
# 模拟天气数据获取
temperature = 72 if units == "imperial" else 22
temp_unit = "°F" if units == "imperial" else "°C"
# 返回当前天气文本信息
return [
{
"type": "text",
"text": f"{location}当前天气:晴天,温度{temperature}{temp_unit},湿度65%",
}
]
# 如果调用的是天气预报工具
elif name == "com.example.weather/forecast":
# 获取城市名称,默认为“未知城市”
location = arguments.get("location", "未知城市")
# 获取预报天数,默认为3天
days = arguments.get("days", 3)
# 模拟天气预报数据
forecast = f"{location}未来{days}天天气预报:\n"
# 循环生成每一天的天气信息
for i in range(days):
forecast += f"第{i+1}天:晴天,温度20-25°C\n"
# 返回天气预报文本信息
return [{"type": "text", "text": forecast}]
# 未知工具,抛出异常
else:
raise ValueError(f"未知工具:{name}")
# 主函数,程序入口
def main():
"""主函数"""
# 创建WeatherServer实例
server = WeatherServer()
# 在标准错误输出服务器启动提示
print("🌤️ 天气服务器已启动,等待连接...", file=sys.stderr)
# 从标准输入读取请求,向标准输出发送响应
for line in sys.stdin:
try:
# 解析输入的JSON请求
request = json.loads(line.strip())
# 处理请求,获取响应
response = server.handle_request(request)
# 输出响应的JSON字符串
print(json.dumps(response, ensure_ascii=False))
# 刷新标准输出缓冲区
sys.stdout.flush()
# 捕获JSON解析错误
except json.JSONDecodeError:
# 输出解析错误响应
print(
json.dumps(
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": None,
"error": {"code": -32700, "message": "Parse error"},
},
ensure_ascii=False,
)
)
# 刷新标准输出缓冲区
sys.stdout.flush()
# 判断是否为主模块,若是则执行main函数
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()7.1.2 🔄 工作流程图 #
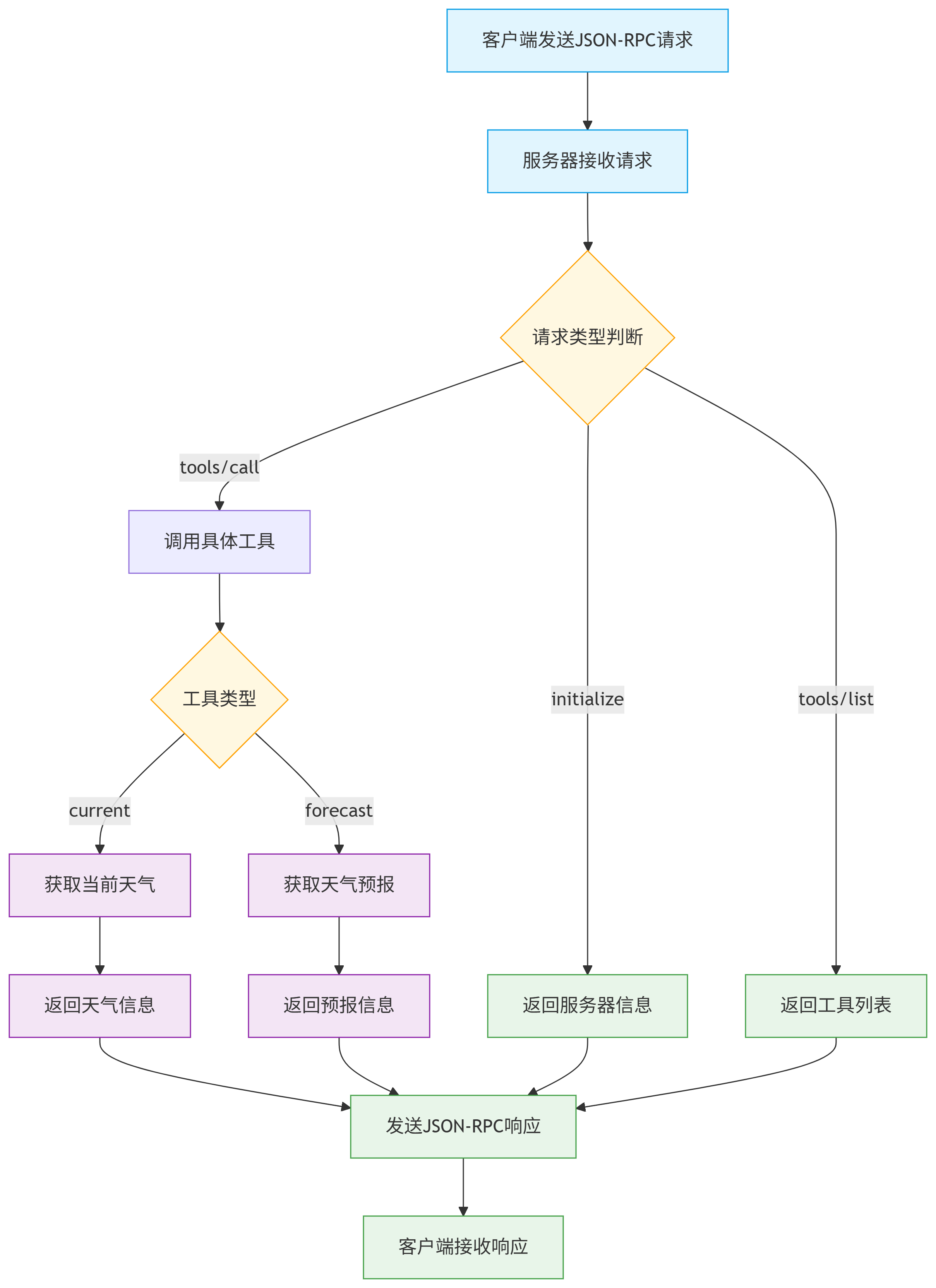
7.1.3 JSON-RPC协议规范 #
7.1.3.1 请求格式示例 #
初始化请求:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "initialize",
"params": {}
}7.1.3.2 工具列表请求: #
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 2,
"method": "tools/list",
"params": {}
}7.1.3.3 工具调用请求: #
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 3,
"method": "tools/call",
"params": {
"name": "com.example.weather/current",
"arguments": {
"location": "北京",
"units": "metric"
}
}
}7.1.3.4 响应格式示例 #
7.1.3.4.1 成功响应: #
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 3,
"result": {
"content": [
{
"type": "text",
"text": "北京当前天气:晴天,温度22°C,湿度65%"
}
]
}
}7.1.3.4.2 错误响应: #
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 3,
"error": {
"code": -32603,
"message": "未知工具:invalid_tool"
}
}7.2 MCP客户端实现 #
7.2.1 weather_client.py #
# 导入json模块,用于处理JSON数据
import json
# 导入subprocess模块,用于创建和管理子进程
import subprocess
# 导入sys模块,用于访问与Python解释器相关的变量和函数
import sys
# 从typing模块导入类型注解
from typing import Dict, Any, List
# 定义天气客户端类
class WeatherClient:
"""天气客户端类"""
# 构造函数,初始化服务器命令
def __init__(self, server_command: List[str]):
# 保存服务器命令
self.server_command = server_command
# 服务器进程对象初始化为None
self.server_process = None
# 工具列表初始化为空
self.tools = []
# 连接到天气服务器
def connect(self):
"""连接到天气服务器"""
try:
# 启动服务器进程,重定向标准输入、输出和错误
self.server_process = subprocess.Popen(
self.server_command,
stdin=subprocess.PIPE,
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.PIPE,
text=True,
bufsize=1,
)
# 初始化连接
self._initialize()
# 获取工具列表
self._get_tools()
# 打印连接成功信息
print(" 成功连接到天气服务器")
# 返回True表示连接成功
return True
# 捕获异常并打印错误信息
except Exception as e:
print(f" 连接服务器失败:{str(e)}")
# 返回False表示连接失败
return False
# 初始化连接
def _initialize(self):
"""初始化连接"""
# 构造初始化请求
request = {"jsonrpc": "2.0", "id": 1, "method": "initialize", "params": {}}
# 发送请求并获取响应
response = self._send_request(request)
# 如果响应中包含result字段
if "result" in response:
# 打印服务器信息
print(f"🌤️ 服务器信息:{response['result'].get('serverInfo', {})}")
# 获取服务器支持的工具列表
def _get_tools(self):
"""获取服务器支持的工具列表"""
# 构造获取工具列表的请求
request = {"jsonrpc": "2.0", "id": 2, "method": "tools/list", "params": {}}
# 发送请求并获取响应
response = self._send_request(request)
# 如果响应中包含result字段
if "result" in response:
# 提取工具列表
self.tools = response["result"].get("tools", [])
# 打印工具数量
print(f" 服务器支持 {len(self.tools)} 个工具")
# 遍历并打印每个工具的标题和描述
for tool in self.tools:
print(
f" - {tool.get('title', '未知工具')}: {tool.get('description', '')}"
)
# 向服务器发送请求并获取响应
def _send_request(self, request: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""向服务器发送请求并获取响应"""
try:
# 将请求对象序列化为JSON字符串
request_str = json.dumps(request, ensure_ascii=False)
# 写入到服务器进程的标准输入
self.server_process.stdin.write(request_str + "\n")
# 刷新输入缓冲区
self.server_process.stdin.flush()
# 读取服务器进程的标准输出
response_line = self.server_process.stdout.readline()
# 如果没有读取到响应
if not response_line:
# 返回错误信息
return {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": request.get("id"),
"error": {"code": -32000, "message": "服务器无响应"},
}
# 返回解析后的JSON响应
return json.loads(response_line.strip())
# 捕获异常并返回错误信息
except Exception as e:
return {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": request.get("id"),
"error": {"code": -32000, "message": f"请求失败:{str(e)}"},
}
# 调用服务器上的工具
def call_tool(self, tool_name: str, arguments: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""调用服务器上的工具"""
# 导入time模块用于生成唯一请求ID
import time
# 生成基于当前时间的请求ID
request_id = int(time.time() * 1000)
# 构造工具调用请求
request = {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": request_id,
"method": "tools/call",
"params": {"name": tool_name, "arguments": arguments},
}
# 打印调用工具的信息
print(f"🔧 调用工具:{tool_name},参数:{arguments}")
# 发送请求并获取结果
result = self._send_request(request)
# 打印收到的响应
print(f"📥 收到响应:{result}")
# 返回结果
return result
# 交互模式
def interactive_mode(self):
"""交互模式"""
# 打印进入交互模式提示
print("\n🎮 进入天气查询交互模式,输入 'quit' 退出")
# 打印可用命令
print("可用命令:")
print(" current <城市名> [metric|imperial]")
print(" forecast <城市名> [天数]")
print(" list_tools")
print(" quit")
# 循环等待用户输入命令
while True:
try:
# 获取用户输入并去除首尾空格
command = input("\n请输入命令: ").strip()
# 如果输入quit则退出循环
if command == "quit":
break
# 如果输入list_tools则列出所有工具
elif command == "list_tools":
for i, tool in enumerate(self.tools, 1):
print(
f"{i}. {tool.get('title', '未知工具')}: {tool.get('description', '')}"
)
# 如果输入以current开头,查询当前天气
elif command.startswith("current "):
# 解析参数
parts = command[8:].strip().split()
# 至少需要一个参数(城市名)
if len(parts) >= 1:
location = parts[0]
# 单位参数可选,默认为metric
units = parts[1] if len(parts) > 1 else "metric"
# 调用current工具
result = self.call_tool(
"com.example.weather/current",
{"location": location, "units": units},
)
# 打印结果
self._print_result(result)
else:
# 参数不足时提示用法
print(" 用法:current <城市名> [metric|imperial]")
# 如果输入以forecast开头,查询天气预报
elif command.startswith("forecast "):
# 解析参数
parts = command[9:].strip().split()
# 至少需要一个参数(城市名)
if len(parts) >= 1:
location = parts[0]
# 天数参数可选,默认为3
days = int(parts[1]) if len(parts) > 1 else 3
# 调用forecast工具
result = self.call_tool(
"com.example.weather/forecast",
{"location": location, "days": days},
)
# 打印结果
self._print_result(result)
else:
# 参数不足时提示用法
print(" 用法:forecast <城市名> [天数]")
# 其他未知命令
else:
print(" 未知命令,请重试")
# 捕获Ctrl+C中断,退出循环
except KeyboardInterrupt:
break
# 捕获其他异常并打印错误信息
except Exception as e:
print(f" 执行命令时出错:{str(e)}")
# 打印工具调用的结果
def _print_result(self, result: Dict[str, Any]):
"""打印工具调用的结果"""
# 打印原始结果
print(f"🔍 解析结果:{result}")
# 如果结果中有result字段
if "result" in result:
# 获取内容列表
content = result["result"].get("content", [])
# 打印内容项数量
print(f" 找到 {len(content)} 个内容项")
# 遍历内容项
for i, item in enumerate(content):
# 如果内容类型为文本,打印文本内容
if item.get("type") == "text":
print(f"📄 内容 {i+1}: {item['text']}")
# 其他类型直接打印
else:
print(f"📄 内容 {i+1}: {item}")
# 如果结果中有error字段,打印错误信息
elif "error" in result:
print(f" 错误:{result['error']['message']}")
# 其他未知格式
else:
print(f"⚠️ 未知响应格式:{result}")
# 断开与服务器的连接
def disconnect(self):
"""断开与服务器的连接"""
# 如果服务器进程存在
if self.server_process:
# 终止服务器进程
self.server_process.terminate()
# 等待服务器进程结束
self.server_process.wait()
# 打印断开连接信息
print(" 已断开与服务器的连接")
# 主程序入口
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 检查命令行参数数量
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
# 打印用法提示
print("使用方法:python weather_client.py <服务器脚本路径>")
print("示例:python weather_client.py weather_server.py")
# 退出程序
sys.exit(1)
# 获取服务器脚本路径
server_script = sys.argv[1]
# 创建WeatherClient实例
client = WeatherClient([sys.executable, server_script])
# 如果成功连接服务器,则进入交互模式
if client.connect():
client.interactive_mode()
# 断开与服务器的连接
client.disconnect()
7.2.2 🔄 工作流程图 #
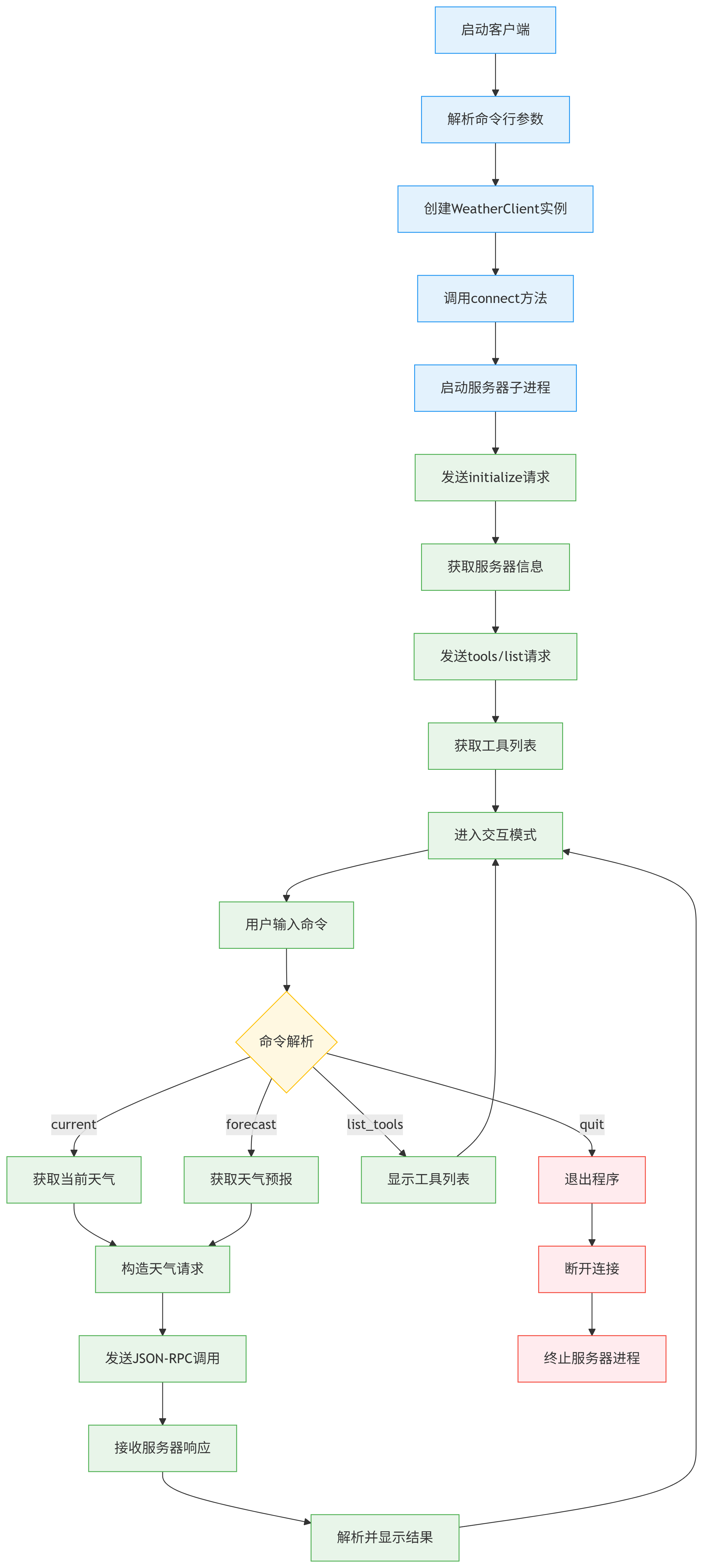
8.🎯 总结 #
MCP架构的核心优势:
8.1 标准化 #
- 统一的协议规范
- 多语言SDK支持
- 开放的生态系统
8.2 灵活性 #
- 支持本地和远程服务器
- 多种传输方式
- 可扩展的原语系统
8.3 实用性 #
- 完整的生命周期管理
- 实时通知机制
- 类型安全的通信
8.4 可扩展性 #
- 模块化设计
- 插件化架构
- 易于集成