1.采样概述 #
Model Context Protocol (MCP) 为服务器提供了一种标准化方式,通过客户端向语言模型请求LLM采样("补全"或"生成")。该流程使客户端能够保持对模型访问、选择和权限的控制,同时让服务器无需API密钥即可利用AI能力。服务器可以请求基于文本、音频或图像的交互,并选择性地在其提示中包含来自MCP服务器的上下文信息。
2.用户交互模型 #
MCP中的采样功能允许服务器通过启用LLM调用来实现代理行为,可以嵌套在其他MCP服务器功能内部。
实现方可以自由选择适合其需求的任何接口模式来公开采样功能——协议本身并未强制规定任何特定的用户交互模型。
2.1 ⚠️ 重要安全提醒 #
出于信任、安全及保障考虑,存在应该始终保持人工介入,并具备拒绝采样请求的能力。
应用程序应该:
- 提供直观易用的用户界面,方便审核抽样请求
- 允许用户在发送前查看并编辑提示内容
- 在交付前展示生成的回复以供审阅
3.功能声明 #
支持采样的客户端必须声明sampling能力期间初始化:
{
"capabilities": {
"sampling": {}
}
}4.协议消息 #
4.1 创建消息 #
为了请求语言模型生成内容,服务器会发送一个sampling/createMessage请求
请求:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "sampling/createMessage",
"params": {
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": {
"type": "text",
"text": "What is the capital of France?"
}
}
],
"modelPreferences": {
"hints": [
{
"name": "claude-3-sonnet"
}
],
"intelligencePriority": 0.8,
"speedPriority": 0.5
},
"systemPrompt": "You are a helpful assistant.",
"maxTokens": 100
}
}响应:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"result": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": {
"type": "text",
"text": "The capital of France is Paris."
},
"model": "claude-3-sonnet-20240307",
"stopReason": "endTurn"
}
}5.消息流 #
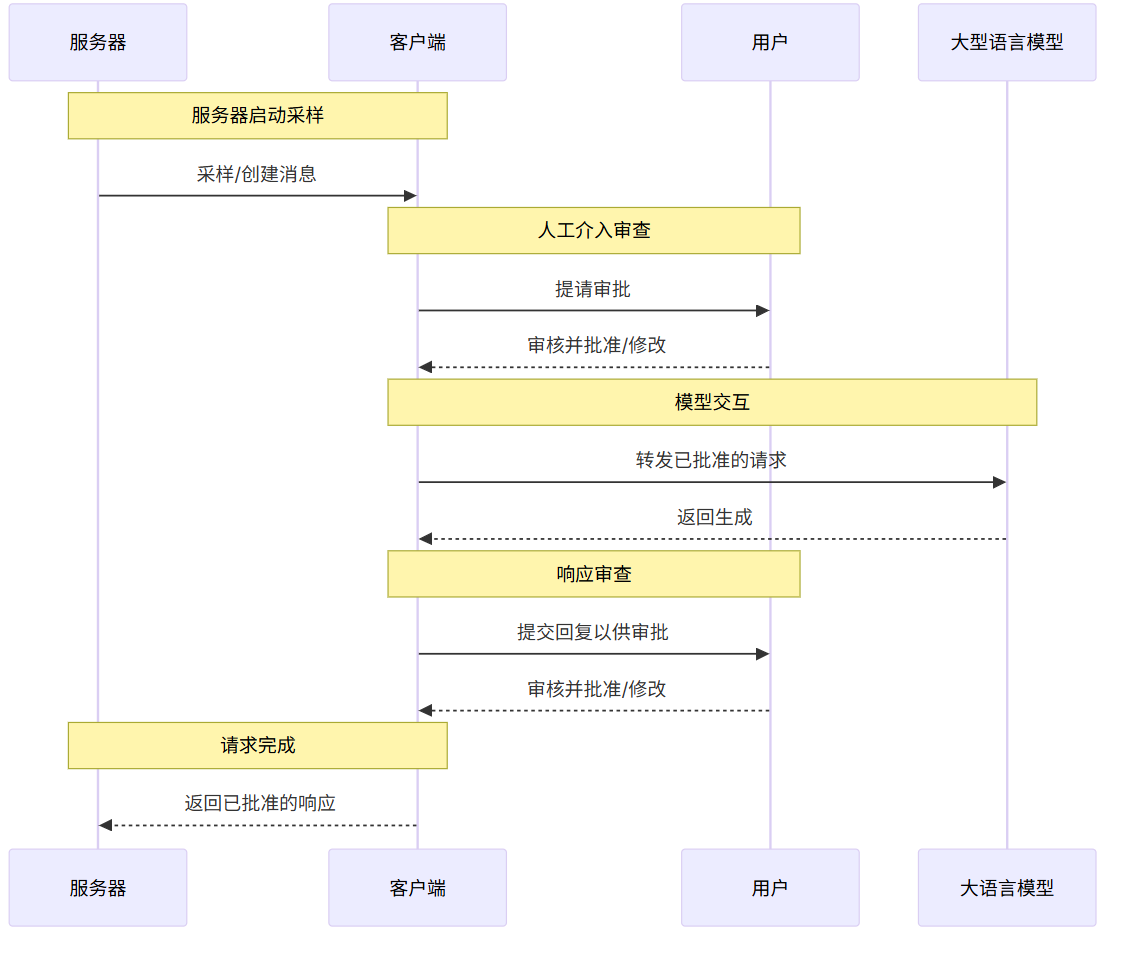
6.数据类型 #
6.1 消息 #
采样消息可能包含:
6.1.1 文本内容 #
{
"type": "text",
"text": "The message content"
}6.1.2 图像内容 #
{
"type": "image",
"data": "base64-encoded-image-data",
"mimeType": "image/jpeg"
}6.1.3 音频内容 #
{
"type": "audio",
"data": "base64-encoded-audio-data",
"mimeType": "audio/wav"
}6.2 模型偏好 #
在MCP中进行模型选择需要谨慎抽象,因为服务器和客户端可能使用不同AI提供商提供的不同模型。服务器不能简单地通过名称请求特定模型,因为客户端可能无法访问该确切模型,或者更倾向于使用其他提供商的等效模型。
为了解决这个问题,MCP实现了一个偏好系统,将抽象能力优先级与可选的模型提示相结合。
6.2.1 能力优先级 #
服务器通过三个标准化优先级值(0-1)来表达其需求:
costPriority- 最小化成本有多重要?数值越高,越倾向于选择更便宜的模型。speedPriority- 低延迟有多重要?数值越高表示更偏好响应速度快的模型。intelligencePriority- 高级功能的重要性如何?数值越高表示更偏好能力更强的模型。
6.2.2 模型提示 #
虽然优先级有助于根据特性选择模型,hints允许服务器建议特定的模型或模型系列。
- 提示被视为可以灵活匹配模型名称的子字符串。
- 多个提示会按优先顺序进行评估
- 客户端可能将提示映射到不同提供商的等效模型
- 提示仅供参考,最终模型选择由客户端决定。
例如:
{
"hints": [
{ "name": "claude-3-sonnet" }, // Prefer Sonnet-class models
{ "name": "claude" } // Fall back to any Claude model
],
"costPriority": 0.3, // Cost is less important
"speedPriority": 0.8, // Speed is very important
"intelligencePriority": 0.5 // Moderate capability needs
}客户端根据这些偏好从其可用选项中选择合适的模型。例如,如果客户端无法访问Claude模型但可以使用Gemini,它可能将十四行诗提示映射到gemini-1.5-pro基于类似的功能。
7.错误处理 #
客户端应该返回常见故障情况下的错误信息
示例错误:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"error": {
"code": -1,
"message": "User rejected sampling request"
}
}8.安全注意事项 #
- 客户端应该实施用户审批控制
- 双方应该验证消息内容
- 客户端应该尊重模型偏好提示
- 客户端应该实施速率限制
- 双方必须妥善处理敏感数据
9.最佳实践 #
9.1 模型选择策略 #
推荐做法:
- 使用优先级系统而非硬编码模型名称
- 提供多个模型提示作为备选方案
- 根据具体用例调整优先级权重
示例:
{
"modelPreferences": {
"hints": [
{"name": "gpt-4"},
{"name": "claude-3"},
{"name": "gemini-pro"}
],
"intelligencePriority": 0.9,
"speedPriority": 0.3,
"costPriority": 0.2
}
}9.2 内容类型处理 #
文本内容:
- 确保文本编码正确(UTF-8)
- 合理设置
maxTokens限制 - 使用清晰的系统提示
多媒体内容:
- 压缩图像以减少传输大小
- 使用适当的MIME类型
- 考虑内容大小限制
9.3 错误处理策略 #
常见错误码:
-1: 用户拒绝请求-2: 模型不可用-3: 内容格式错误-4: 速率限制-5: 权限不足
错误响应示例:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"error": {
"code": -2,
"message": "Requested model not available",
"data": {
"availableModels": ["claude-3-haiku", "gpt-3.5-turbo"]
}
}
}10.常见问题解答 #
10.1 Q: 如何处理模型不可用的情况? #
A: 客户端应该:
- 首先尝试使用提供的模型提示
- 如果失败,根据优先级选择替代模型
- 返回错误信息说明模型选择
10.2 Q: 多媒体内容的大小限制是多少? #
A: 具体限制取决于客户端实现,但建议:
- 图像:不超过10MB
- 音频:不超过50MB
- 文本:不超过100KB
10.3 Q: 如何实现安全的用户审批流程? #
A: 建议实现:
- 清晰的用户界面显示请求内容
- 允许用户编辑提示
- 提供拒绝和批准选项
- 记录所有操作日志
10.4 Q: 如何处理长时间运行的请求? #
A: 考虑:
- 实现超时机制
- 提供进度指示
- 允许用户取消请求
- 使用流式响应(如果支持)
11.实现示例 #
11.1 Python 客户端示例 #
# 导入json模块,用于处理JSON数据
import json
# 导入base64模块,用于进行base64编码
import base64
# 从typing模块导入类型注解List、Dict、Any
from typing import List, Dict, Any
# 定义MCPClient类
class MCPClient:
# 构造函数,初始化采样能力
def __init__(self):
# 声明客户端支持的能力为sampling
self.capabilities = {"sampling": {}}
# 创建采样消息请求的方法
def create_message(self,
messages: List[Dict],
model_preferences: Dict = None,
system_prompt: str = None,
max_tokens: int = 1000) -> Dict:
"""
创建采样消息请求
"""
# 构造请求字典
request = {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": self._get_next_id(),
"method": "sampling/createMessage",
"params": {
"messages": messages,
"maxTokens": max_tokens
}
}
# 如果指定了模型偏好,则添加到请求参数中
if model_preferences:
request["params"]["modelPreferences"] = model_preferences
# 如果指定了系统提示,则添加到请求参数中
if system_prompt:
request["params"]["systemPrompt"] = system_prompt
# 返回构造好的请求
return request
# 添加图像内容到消息的方法
def add_image_content(self, image_path: str, mime_type: str = "image/jpeg") -> Dict:
"""
添加图像内容到消息
"""
# 以二进制方式打开图像文件
with open(image_path, "rb") as f:
# 读取文件内容并进行base64编码
image_data = base64.b64encode(f.read()).decode()
# 返回包含图像内容的字典
return {
"type": "image",
"data": image_data,
"mimeType": mime_type
}
# 获取下一个请求ID的方法
def _get_next_id(self) -> int:
# 如果没有_id_counter属性,则初始化为0
if not hasattr(self, '_id_counter'):
self._id_counter = 0
# 递增ID计数器
self._id_counter += 1
# 返回当前ID
return self._id_counter11.2 JavaScript 服务器示例 #
// 定义MCPServer类
class MCPServer {
// 构造函数,初始化采样能力
constructor() {
// 声明服务器支持的能力为sampling
this.capabilities = {
sampling: {}
};
}
// 处理采样请求的异步方法
async handleSamplingRequest(request) {
// 从请求参数中解构出messages、modelPreferences、systemPrompt和maxTokens
const { messages, modelPreferences, systemPrompt, maxTokens } = request.params;
// 验证请求格式是否合法
if (!this.validateRequest(request)) {
// 如果不合法,返回格式错误的响应
return this.createErrorResponse(request.id, -3, "Invalid request format");
}
// 构建模型偏好参数
const preferences = this.buildModelPreferences(modelPreferences);
// 尝试将请求发送到客户端
try {
// 调用sendToClient方法发送采样请求
const response = await this.sendToClient({
method: "sampling/createMessage",
params: {
messages,
modelPreferences: preferences,
systemPrompt,
maxTokens
}
});
// 返回客户端的响应
return response;
} catch (error) {
// 捕获异常并返回错误响应
return this.createErrorResponse(request.id, -1, error.message);
}
}
// 构建模型偏好参数的方法
buildModelPreferences(preferences) {
// 返回包含模型提示和优先级的对象,若未指定则使用默认值
return {
hints: preferences?.hints || [],
intelligencePriority: preferences?.intelligencePriority || 0.5,
speedPriority: preferences?.speedPriority || 0.5,
costPriority: preferences?.costPriority || 0.5
};
}
// 验证请求格式的方法
validateRequest(request) {
// 检查params中是否包含messages,且messages为非空数组
return request.params?.messages &&
Array.isArray(request.params.messages) &&
request.params.messages.length > 0;
}
// 创建错误响应的方法
createErrorResponse(id, code, message) {
// 返回符合JSON-RPC规范的错误对象
return {
jsonrpc: "2.0",
id,
error: { code, message }
};
}
}12.总结 #
MCP采样功能提供了一个强大而灵活的框架,用于在客户端和服务器之间进行AI模型交互。通过遵循本文档中的最佳实践和安全指南,开发者可以构建安全、可靠且用户友好的MCP应用程序。
关键要点:
- 始终实施用户审批机制
- 使用优先级系统而非硬编码模型名称
- 正确处理错误和异常情况
- 遵循安全最佳实践
- 提供清晰的用户界面和反馈